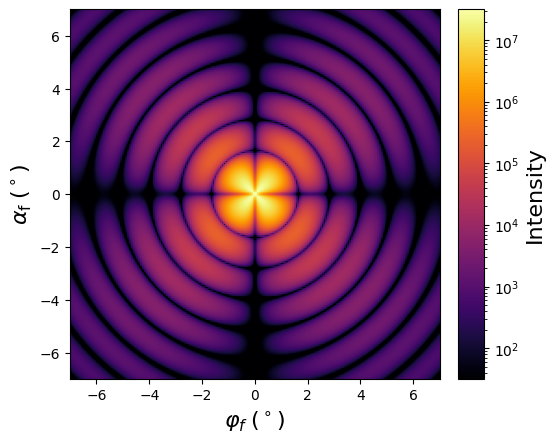
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Simple example demonstrating how polarized SANS experiments can be
simulated with BornAgain.
"""
import bornagain as ba
from bornagain import ba_plot as bp, deg, nm, R3
def get_sample():
"""
A sample with a magnetic core-shell particle in a solvent.
"""
# Materials
B = R3(0, 1e7, 0)
material_Core = ba.RefractiveMaterial("Core", 6e-06, 2e-08, B)
material_Shell = ba.RefractiveMaterial("Shell", 1e-07, 2e-08)
material_Solvent = ba.RefractiveMaterial("Solvent", 5e-06, 0)
# Form factors
ff_1 = ba.Sphere(10*nm)
ff_2 = ba.Sphere(12*nm)
# Particles
particle_1 = ba.Particle(material_Core, ff_1)
particle_1_position = R3(0, 0, 2*nm)
particle_1.translate(particle_1_position)
particle_2 = ba.Particle(material_Shell, ff_2)
# Core shell particles
particle = ba.CoreAndShell(particle_1, particle_2)
# Particle layouts
layout = ba.ParticleLayout()
layout.addParticle(particle)
layout.setTotalParticleSurfaceDensity(0.01)
# Layers
layer = ba.Layer(material_Solvent)
layer.addLayout(layout)
# Sample
sample = ba.MultiLayer()
sample.addLayer(layer)
return sample
def get_simulation(sample):
"""
A polarized SANS simulation
"""
n = 200
# Beam from above (perpendicular to sample):
beam = ba.Beam(1e9, 0.4*nm, 0.001*deg)
# Detector opposite to source:
detector = ba.SphericalDetector(n, -7*deg, 7*deg, n, -7*deg, 7*deg)
beam.setPolarization(R3(0, 1, 0))
detector.setAnalyzer(R3(0, -1, 0))
return ba.ScatteringSimulation(beam, sample, detector)
if __name__ == '__main__':
sample = get_sample()
simulation = get_simulation(sample)
result = simulation.simulate()
bp.plot_simulation_result(result)
bp.show_or_export()
|
 BornAgain
≻ git-main
≻ Documentation ≻ Script examples ≻ Simulation ≻ Scattering in 2d ≻ Polarized SANS
BornAgain
≻ git-main
≻ Documentation ≻ Script examples ≻ Simulation ≻ Scattering in 2d ≻ Polarized SANS